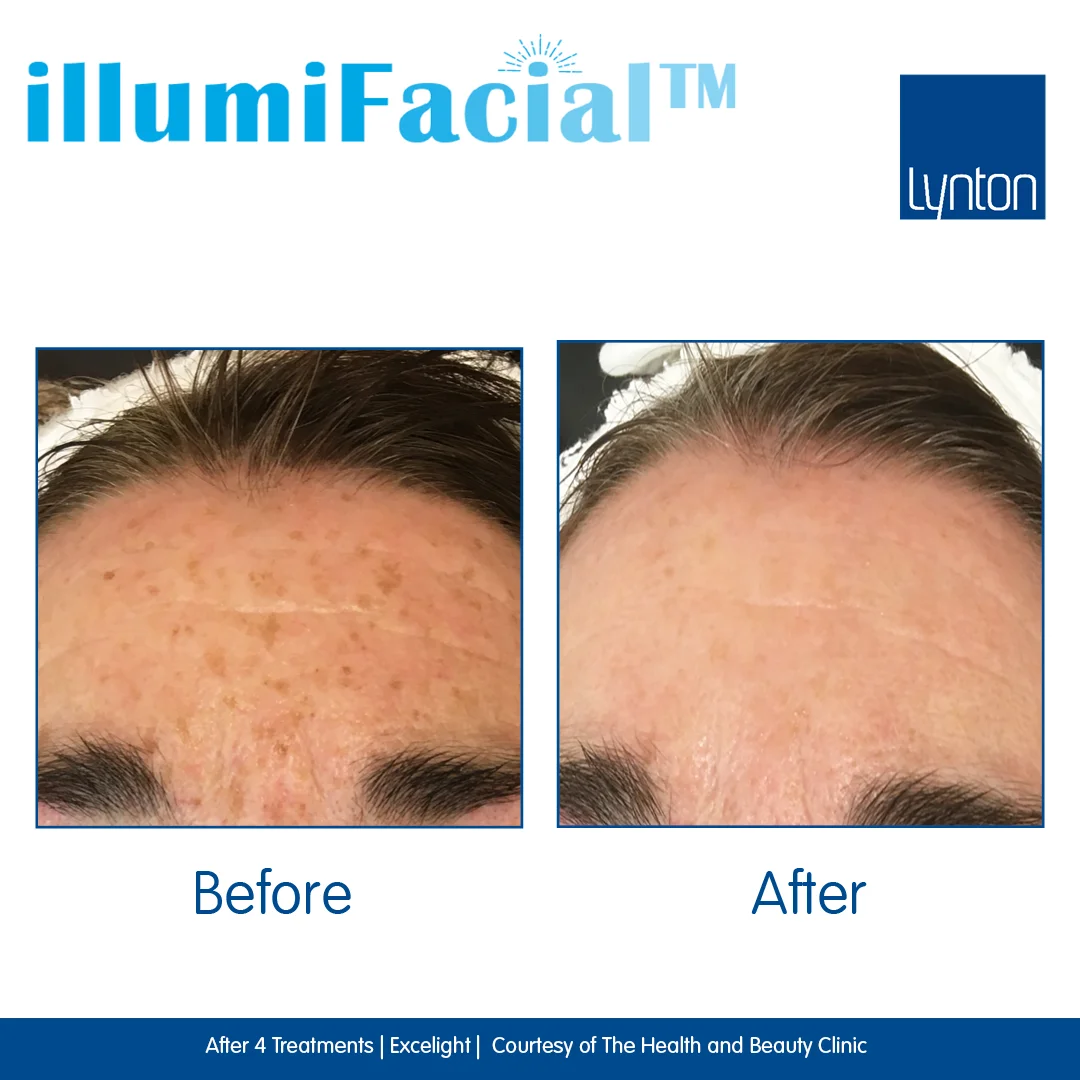
Hyperpigmentation occurs when excess melanin is produced in response to inflammation, sun exposure, or hormonal changes. Common forms include sun spots, post-inflammatory marks, and melasma. Ingredients like vitamin C, kojic acid, and alpha arbutin inhibit enzyme tyrosinase to reduce pigment formation. Regular exfoliation with AHAs or BHAs helps slough away darkened cells, while consistent sunscreen use prevents new spots from forming.\n\nFor more stubborn pigmentation, consider professional treatments such as chemical peels, intense pulsed light (IPL), or laser therapy, which target deeper pigment concentrations. Always perform a patch test and work with a qualified practitioner to minimize risks like post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Maintain results with a comprehensive at-home routine and diligent sun protection to keep your complexion clear and evenly toned.
CONTACT
- +44 20 8626 7869
- info@indermskinclinic.com
- 538 Chiswick High Rd., Chiswick, London W4 5RG, United Kingdom